- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- 1) The Pro Mindset: Search Like a Filter Engineer
- 2) Essential Operators (The 80/20 Set)
- A) Exact phrase with quotes: "..."
- B) Exclude noise with minus: -word
- C) Either/or with OR: term OR term
- D) Search inside a website: site:example.com
- E) Find PDFs, PPTs, DOCs fast: filetype:pdf
- F) Use Google’s Advanced Search pages (when you want UI filters)
- 3) Copy-Paste Search Recipes (Real-World Templates)
- Recipe 1: Find an official document or guideline PDF
- Recipe 2: Search within a company’s help center
- Recipe 3: Find a research-backed explanation (not a random blog)
- Recipe 4: Find a specific file you once saw
- Recipe 5: Troubleshoot errors like a developer
- Recipe 6: Compare products without marketing fluff
- Recipe 7: Find price history / trend context
- Recipe 8: Find slides and presentations
- Recipe 9: Force a cleaner “literal” search when Google gets “too smart”
- 4) Filters That Make Results 10× Better
- A) Filter by date (freshness)
- B) Filter by region & language
- C) Switch verticals: Web → Images → News → Videos
- 5) Special Google Tools Most People Ignore
- A) Google Lens (Search what you see)
- B) Google Alerts (make Google monitor the web for you)
- C) Google Scholar (academic, credible, citable)
- D) Google Patents (inventors, filings, technical detail)
- E) Google Books (snippets + old sources)
- F) Dataset Search (for data hunters)
- G) Google Trends (validate interest + seasonality)
- 6) Verify Results Faster (Avoid Garbage + Misinformation)
- A) Use “About this result” before you click
- B) Cross-check in 30 seconds
- C) Spot and remove personal info exposure
- D) Turn on SafeSearch when needed
- 7) Build Your Personal “Search System”
- A) Keep a tiny “query toolbox”
- B) Use Google’s own operator basics (official help)
- C) Turn “hard searches” into 2 steps
- D) When the answer is moving fast, use Alerts instead of re-searching
- FAQ
- 1) What are the most important Google search operators to learn first?
- 2) Why does Google sometimes ignore what I type and show “similar” results?
- 3) How do I find only PDFs or official documents?
- 4) How do I search within a website that has a terrible internal search?
- 5) How do I verify if an image is old or reused?
- 6) What’s the best Google tool for academic research?
- 7) Can I get Google to notify me when something new is published?
- 8) How can I personalize news sources in Google Search?
- References
Most people use Google like a guessing game: type a few words, scroll, click, back, repeat. Pros use Google like a filter engine—they tell it exactly what to include, what to exclude, which site to search, which file type to prefer, and how recent the results should be.
This guide gives you the high-impact Google Search tricks that actually save time in real life—whether you’re researching, troubleshooting, shopping smarter, verifying images, or hunting down that one PDF you know exists somewhere.
Key Takeaways
- Use operators (like
site:,filetype:, quotes, and minus) to cut noise instantly. - Use filters (time range, region, verbatim) to make results more relevant and current.
- Use specialized Google tools (Scholar, Patents, Books, Alerts, Trends, Lens) for “hard mode” searches.
- Use templates you can copy/paste for faster research and troubleshooting.
1) The Pro Mindset: Search Like a Filter Engineer
When a search feels “hard,” it’s usually because your query is missing one (or more) of these:
- Scope: Where should Google look? (a specific site, domain type, or section)
- Precision: Which words must appear exactly? Which must not appear?
- Format: Are you hunting a PDF, a PPT, a spreadsheet, a support page?
- Freshness: Do you want this year, this month, or a specific time window?
- Intent: Are you researching, buying, learning, fixing, verifying, or comparing?
Instead of adding more words randomly, pros add constraints. Constraints tell Google what to ignore—so what remains is closer to the answer.
2) Essential Operators (The 80/20 Set)
These are the operators that deliver the biggest time savings with the least learning. You can combine them like Lego blocks.
A) Exact phrase with quotes: "..."
Quotes tell Google: “Find this phrase exactly.” Perfect for:
- Finding the original source of a quote
- Searching error messages
- Locating a specific sentence you remember
Example: "This app has been blocked"
B) Exclude noise with minus: -word
Minus removes unwanted meanings and spammy categories.
Example: jaguar speed -car -football
C) Either/or with OR: term OR term
Use OR when people may use different words for the same thing.
Example: resume OR "cv" template site:.edu
D) Search inside a website: site:example.com
site: is one of the most powerful operators ever. Use it to search:
- a specific website you trust
- a documentation portal
- government/education domains:
site:.gov,site:.edu
Examples:
privacy settings site:support.google.comapi rate limit site:developers.google.comtax slab site:incometax.gov.in
E) Find PDFs, PPTs, DOCs fast: filetype:pdf
When you want a guide, report, or form—filetype: is your shortcut.
Examples:
solar policy india filetype:pdfproject proposal template filetype:pptannual report 2025 filetype:pdf site:.com
F) Use Google’s Advanced Search pages (when you want UI filters)
If you prefer checkboxes and dropdowns instead of typing operators, use:
- Google Advanced Search: https://www.google.com/advanced_search
- Advanced Image Search: https://www.google.com/advanced_image_search
- Advanced Book Search: https://books.google.com/advanced_book_search
3) Copy-Paste Search Recipes (Real-World Templates)
Use these like ready-made “search spells.” Replace the placeholders and go.
Recipe 1: Find an official document or guideline PDF
"YOUR TOPIC" filetype:pdf site:.gov
Example: "food safety" filetype:pdf site:.gov
Recipe 2: Search within a company’s help center
YOUR ISSUE site:support.example.com
Example: refund policy site:support.google.com
Recipe 3: Find a research-backed explanation (not a random blog)
YOUR TOPIC site:.edu OR site:.ac OR site:.gov
Recipe 4: Find a specific file you once saw
"EXACT TITLE" filetype:pdf
Or if you remember the site:
"EXACT TITLE" filetype:pdf site:example.com
Recipe 5: Troubleshoot errors like a developer
"PASTE THE EXACT ERROR MESSAGE" -pinterest -quora
Tip: Putting the error in quotes prevents “close enough” results.
Recipe 6: Compare products without marketing fluff
PRODUCT A vs PRODUCT B review -sponsored -affiliate
Recipe 7: Find price history / trend context
YOUR PRODUCT price history
Then use Trends for broader interest signals: https://trends.google.com/trends/
Recipe 8: Find slides and presentations
YOUR TOPIC filetype:ppt OR filetype:pptx
Recipe 9: Force a cleaner “literal” search when Google gets “too smart”
On desktop results, open Tools → switch “All results” to Verbatim (when available). This can help when Google keeps rewriting your intent.
4) Filters That Make Results 10× Better
A) Filter by date (freshness)
For anything time-sensitive (AI tools, pricing, laws, tech updates), filter results by time:
- Search normally
- Click Tools
- Use Any time → Past hour / 24 hours / week / month / year / custom range (availability can vary by device/region)
B) Filter by region & language
If you’re looking for country-specific results (policy, forms, prices, local providers), use Advanced Search and set region/language filters.
Advanced Search: https://www.google.com/advanced_search
C) Switch verticals: Web → Images → News → Videos
Sometimes your answer isn’t on the “All” tab:
- Images: great for identifying objects, products, screenshots, posters
- News: for trending updates and breaking changes
- Videos: for tutorials and real demos
Google News: https://news.google.com/
5) Special Google Tools Most People Ignore
When your search is “serious,” use specialized engines built for that exact content type.
A) Google Lens (Search what you see)
Lens is your shortcut for:
- Reverse image search (is this photo old? where else is it used?)
- Product identification
- Text extraction from images/screenshots
Lens home: https://lens.google/
Lens explained: https://search.google/intl/en-IN/ways-to-search/lens/
How to search with an image (help): https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/1325808
B) Google Alerts (make Google monitor the web for you)
Set alerts for:
- your name/brand
- competitors
- new product launches
- policy changes
Create Alerts: https://www.google.com/alerts
Help guide: https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/4815696
C) Google Scholar (academic, credible, citable)
Use Scholar when you want research papers, citations, and “cited by” chains:
About Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/about.html
D) Google Patents (inventors, filings, technical detail)
Great for deep tech research and prior art:
E) Google Books (snippets + old sources)
Perfect when the best explanation is in a book, magazine, or archived text:
https://books.google.com/advanced_book_search
F) Dataset Search (for data hunters)
When you need datasets for ML, research, or analysis:
https://datasetsearch.research.google.com/
G) Google Trends (validate interest + seasonality)
Use Trends to understand if a topic is rising, falling, seasonal, or regional:
https://trends.google.com/trends/
6) Verify Results Faster (Avoid Garbage + Misinformation)
Finding information is easy. Finding reliable information is the real skill.
A) Use “About this result” before you click
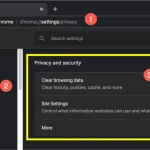
On many results, you can open the “More” (three dots) panel to see context about the source. This is useful when you don’t recognize the website.
Google also shares verification features and context tools here:
https://blog.google/products/search/google-search-new-fact-checking-misinformation/
B) Cross-check in 30 seconds
- Open 2–3 credible sources (not just one).
- Prefer original sources (official docs, research, primary announcements).
- Use time filters to avoid outdated pages.
C) Spot and remove personal info exposure
If you find your personal contact info showing in Search results, Google provides reporting flows and guidance:
https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/12719076
D) Turn on SafeSearch when needed
SafeSearch can filter explicit results (useful for families, schools, shared devices):
- SafeSearch settings: https://www.google.com/safesearch
- Help guide: https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/510
7) Build Your Personal “Search System”
The best trick isn’t a secret operator—it’s a repeatable workflow.
A) Keep a tiny “query toolbox”
Save these in a notes app so you can reuse them:
site:+ a trusted domain (support pages, docs portals)filetype:pdffor guides/reports- Quotes for error messages
- Minus terms you always exclude (e.g.,
-pinterest -template -free)
B) Use Google’s own operator basics (official help)
Google’s help pages mention using operators like quotes, minus, and site: (and Advanced Search as a UI option). Start there, then experiment carefully with additional operators that may work in practice.
Operator basics: https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/2466433
Advanced Search help: https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/35890
C) Turn “hard searches” into 2 steps
Step 1: Find one credible page on the topic.
Step 2: Search within that site using site: to expand.
Example:
- Find a relevant Google Developers doc → then:
your topic site:developers.google.com
D) When the answer is moving fast, use Alerts instead of re-searching
For evolving topics (security updates, app policy changes, new tools), set an alert and let the web come to you.
FAQ
1) What are the most important Google search operators to learn first?
Start with quotes ("exact phrase"), minus (-exclude), OR, site:, and filetype:. These cover most real-world needs.
2) Why does Google sometimes ignore what I type and show “similar” results?
Google tries to interpret intent (spelling corrections, synonyms, “close matches”). If that hurts your search, use quotes and try “Verbatim” under Tools (when available).
3) How do I find only PDFs or official documents?
Use filetype:pdf and restrict with site: (for example, site:.gov or a specific department domain).
4) How do I search within a website that has a terrible internal search?
Use Google with site:thewebsite.com. This often beats the site’s own search.
5) How do I verify if an image is old or reused?
Use Google Lens or “search with an image” to find where else it appears online and to locate older versions.
6) What’s the best Google tool for academic research?
Google Scholar. It shows citations and lets you follow “cited by” trails to newer research.
7) Can I get Google to notify me when something new is published?
Yes—Google Alerts can email you when new results match your keywords.
8) How can I personalize news sources in Google Search?
For news-related queries, Google has a “Preferred sources” feature in Top stories in many regions that lets you prioritize publishers you trust (availability may vary).
References
- Google Search Help — Refine web searches (operators): https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/2466433
- Google Search Help — Advanced Search: https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/35890
- Google Advanced Search page: https://www.google.com/advanced_search
- Google Alerts: https://www.google.com/alerts
- Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/
- Google Lens: https://lens.google/
- Search with an image (help): https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/1325808
- Google Patents: https://patents.google.com/
- Dataset Search: https://datasetsearch.research.google.com/
- Google Trends: https://trends.google.com/trends/